All we know is a rugged history about earth and how it came to its current existing state. This existence is, however, not very healthy and thus have led scientists into incessant work on researches and further studies in order to start with earth’s recovery.
A very important aspect of this recovery is reconstruction of the global climate.
Subsequently full-swing evaluations on this matter have been done which provided results stating that scientists have been successful to reconstruct the earth’s temperature back to the one from the last Ice Age.
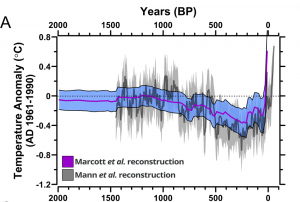
Initially, the climatic reconstruction was region-specific, but later around 73 global sites were studied by Shaun Marcott from Oregon State’s College for a broader inspection of the impact. The revelation is such that Earth has become warmer, in fact 70-80% more than approximately 11,000 years ago. Another observation of this study is that mostly the northern hemisphere has undergone drastic climatic evolution lately because of the population density and industrial developments along with the quicker pace in the last decade. Marcott states that the study was expected as-‘became cooler’ in the summers of Northern Hemisphere after the change in Earth’s orientation since the Holocene period but ‘obviously, we are not’.
The fossils from terrestrial and oceanic archives are studied to understand both Earth’s history as well as the differences in the climatic variation through the years from their chemical and physical composition particularly isotopic ratios. Another factor to Earth’s climatic reshaping is due to the increase in CO2 and green house emissions into the atmosphere. A rampant change in global temperature is evident in the last 100 years such that there are confirmed chances of increase from 2 to 11.5 degrees by this century.
Naturally occurring isotopes are one of the common ways of digging into Earth’s biography. Oxygen has two common isotopes namely oxygen-16 and oxygen-18, the former one is lighter and is found in seawater during summers but when the Earth cools down it changes its state to ice evaporated at higher latitudes while the latter is present in the atmosphere in a proportion with oxygen-16 to produce an ‘ice volume effect’, in other words reflection of Earth’s climate and this is used for climatic reconstruction.
Scientists have found yet another way to study Earth’s history other than archaeology. It is the ice cores which are found to be indicators of past temperatures. In laboratories, samples of ices from landmasses like Greenland and Antarctica can be measured to identify their chemical properties- the amount of oxygen, carbon dioxide and nitrogen present in the atmospheric state they were buried in. These empirical data are then calculated with their heat holding capacity in the atmosphere to trace the past temperatures.
Rather than the geographically constrained clams and corals, the single-celled ‘Foraminifera’ that occurs oceanic, everywhere can be studied as an “exquisite fossil record”. Accurate proceedings and measurements can lead to the exact goal of global climatic understanding and then subsequent reconstruction for a healthy fit Earth.
It is a step as significant as learning about Earth’s past and present because we are assigned citizens of this green planet.
Credits: About History- blogger, The Atlantic eurekalert.org smithsonianmag.com














Add Comment